Introduction to DBT Tool & Install and Running in EC2 machine
What is DBT?
DBT (data build tool) enables analytics engineers to transform data in their warehouses by simply writing select statements. DBT handles turning these select statements into tables and views. DBT does the T in ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) processes – it doesn’t extract or load data, but it’s extremely good at transforming data that’s already loaded into your warehouse.
There’s two main ways of working with DBT
DBT Core is the software that takes a DBT project (.sql and .yml files) and a command and then creates tables/views in your warehouse. DBT Core includes a command line interface (CLI) so that users can execute DBT commands using a terminal program. DBT Core is open source and free to use.
DBT Cloud is an application that helps teams use DBT. DBT Cloud provides a web-based IDE to develop DBT projects, a purpose-built scheduler, and a way to share DBT documentation with your team. DBT Cloud offers a number of features for free, as well as additional features in paid tiers (check out the pricing here).
Database Connections
DBT connects to your data warehouse to run data transformation queries. As such, you’ll need a data warehouse with source data loaded in it to use DBT. DBT natively supports connections to Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift and Postgres data warehouses
Project:
A DBT project is a directory of .sql and .yml files, which DBT uses to transform your data. At a minimum, a DBT project must contain:
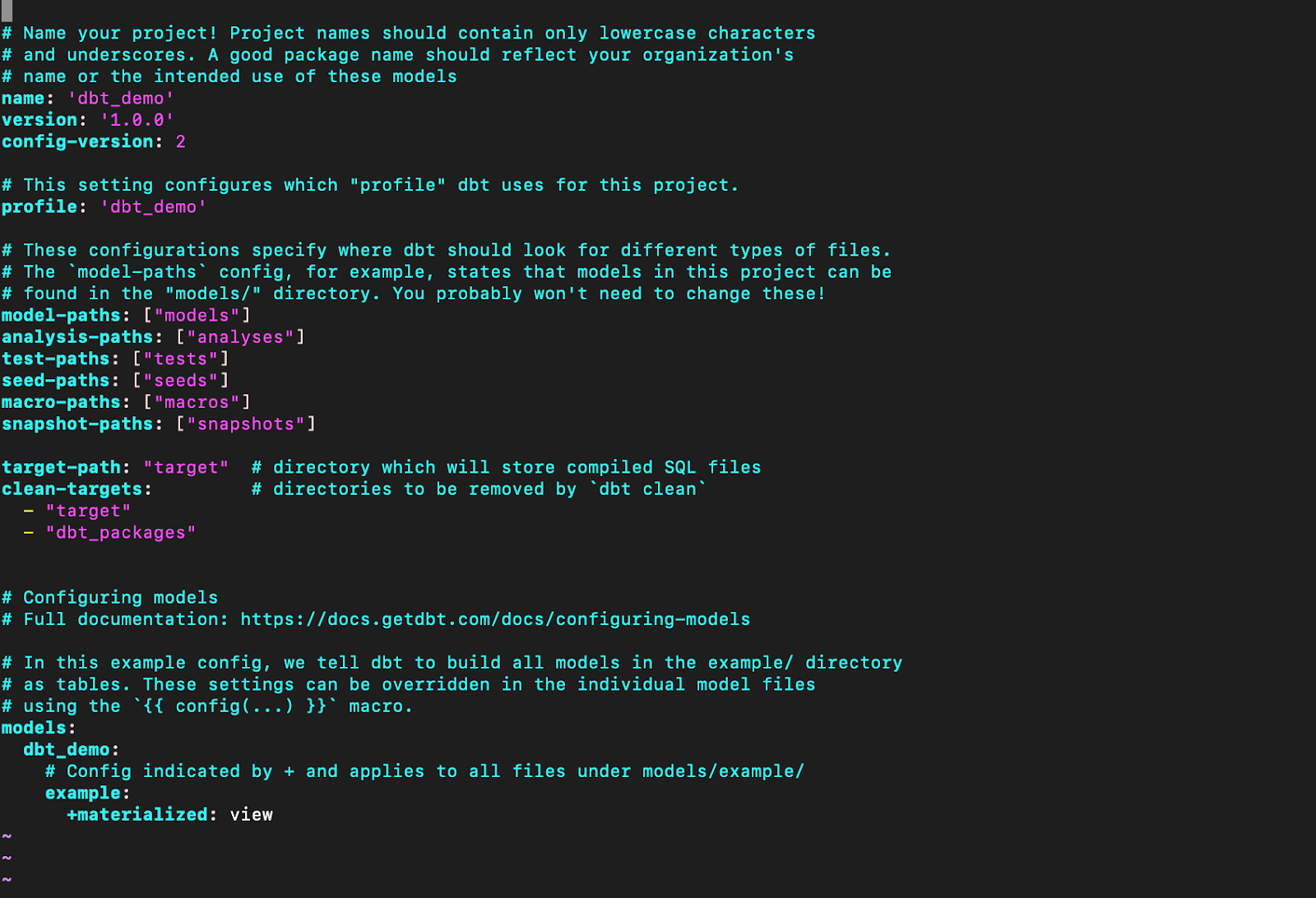
- A project file: A DBT_project.yml file tells DBT that a particular directory is a DBT project, and also contains configurations for your project.
- Models: A model is a single .sql file. Each model contains a single select statement that either transforms raw data into a dataset that is ready for analytics, or, more often, is an intermediate step in such a transformation. A project may also contain a number of other resources, such as snapshots, seeds, tests, macros, documentation, and sources.
Developing locally with the Command Line Interface (CLI)
To use the CLI:
Prerequisite - Create the EC2 Machine
Steps to Set up DBT core (i) Install DBT in Amazon EC2 Machine. For this demo installing DBT-snowflake Inorder to install DBT we need pip so first install pip
1
2
→ sudo apt update
→ sudo apt install python3-pip
1
2
3
Install the DBT with adapter
pip install \ DBT-core \ DBT-postgres \ DBT-redshift \ DBT-snowflake \ DBT-bigquery
pip install DBT-snowflake
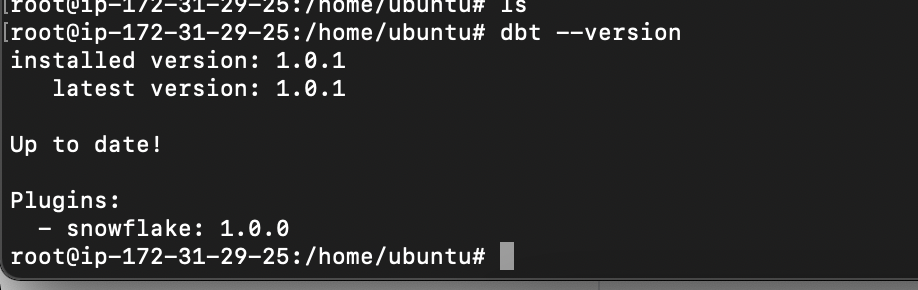
Verify the DBT version
1
dbt -version
Result:
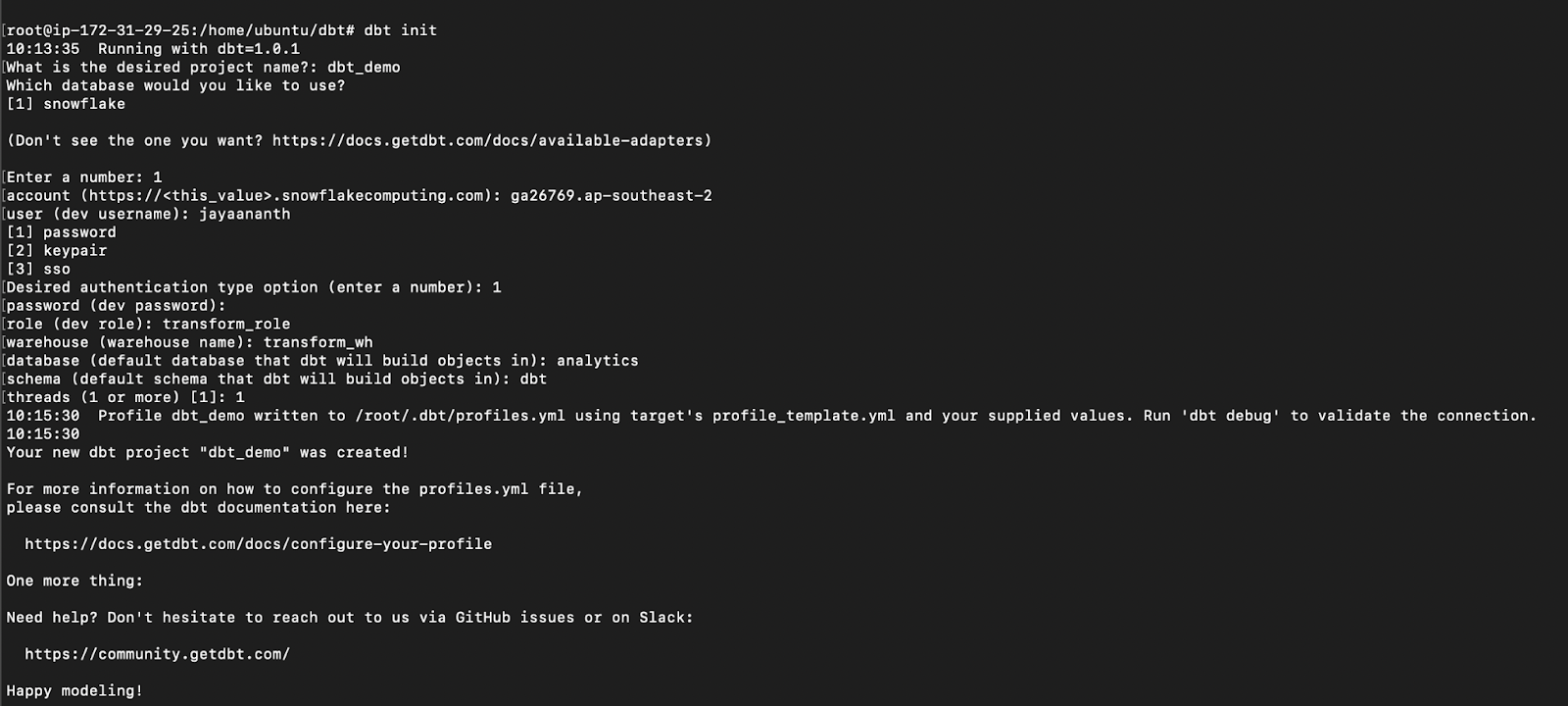
(ii) Initialise the DBT init (DBT init [project-name])and provide the connection details or it can be manually updated too (/root/.DBT/profiles.yml)
1
dbt init
Result:
(iii) After the DBT init command the list of module folder will be created ls -ltr
Result:
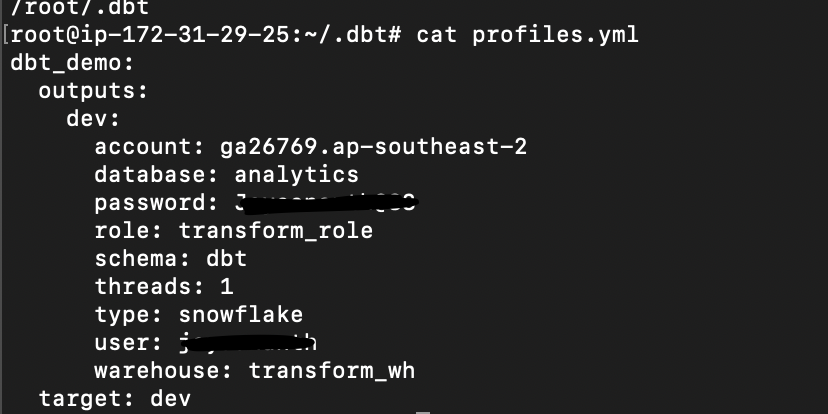
(iv) To verify the credential details go to profile.yml file
1
2
cd /root/.DBT
cat profiles.yml
Result:
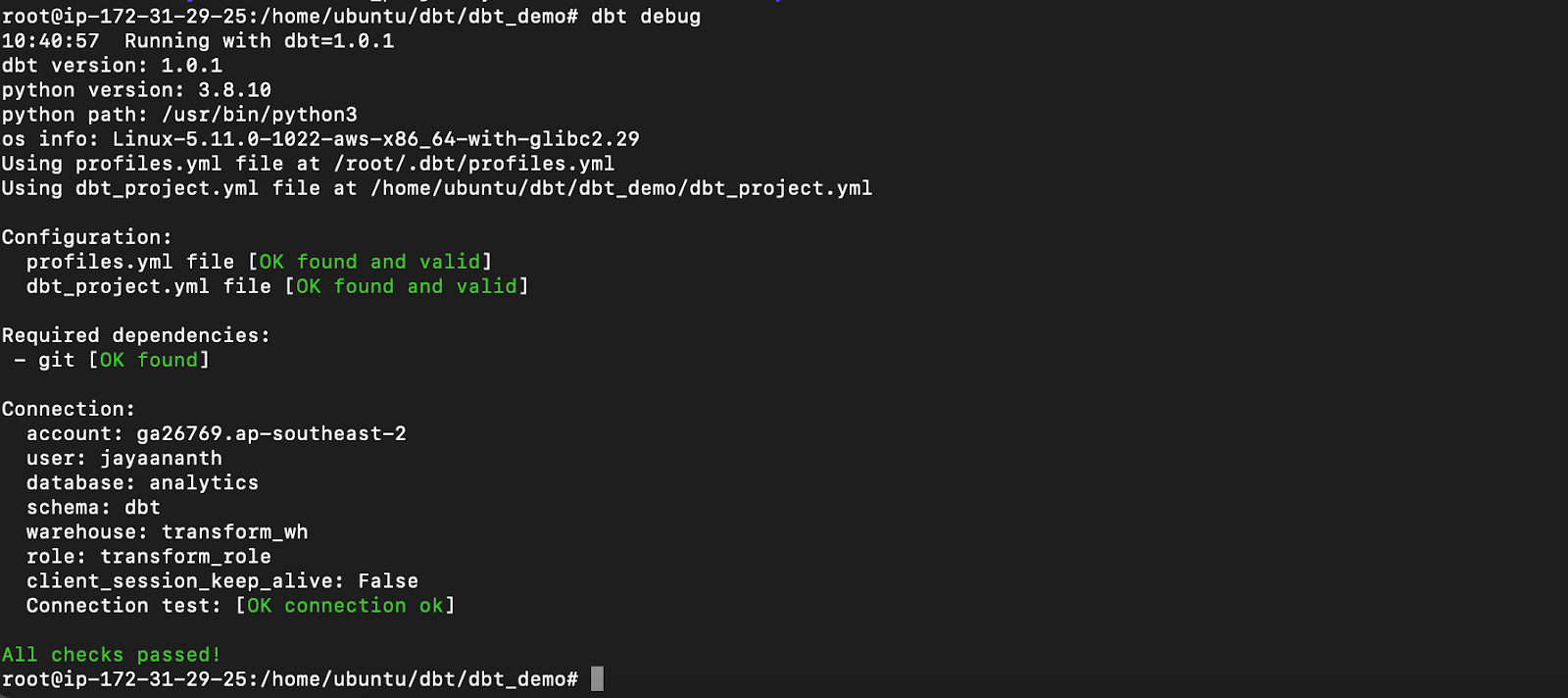
(v) run DBT debug to verify the connectivity
Command:
1
dbt debug
Result:
(vi) Verify the dbt_profile .yml file contains all the details of the project
Command:
1
cat dbt_profile.yml
Result:
Model:
A model is a select statement. Models are defined in .sql files (typically in your models directory): Each .sql file contains one model / select statement The name of the file is used as the model name Models can be nested in subdirectories within the models directory When you execute the DBT run command, DBT will build this model in your data warehouse by wrapping it in a create view as or create table as statement.
Materializations:
Materializations are strategies for persisting DBT models in a warehouse. There are four types of materializations built into DBT. They are:
- table
- view
- incremental
- ephemeral
(vii) Under the model please write the Select statement and declare the materialised as view or table
1
cat my_first_dbt_model.sql
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
with source_data as (
select 1 as id, 'NJ' as state, '2020-02-01 00:01:00.000'::timestamp as updated_at
union all
select null as id, 'CT' as state, '2020-01-01 00:00:00.000'::timestamp as updated_at
union all
select 4 as id, 'VT' as state, '2020-01-01 00:00:00.000'::timestamp as updated_at
)
select *
from source_data
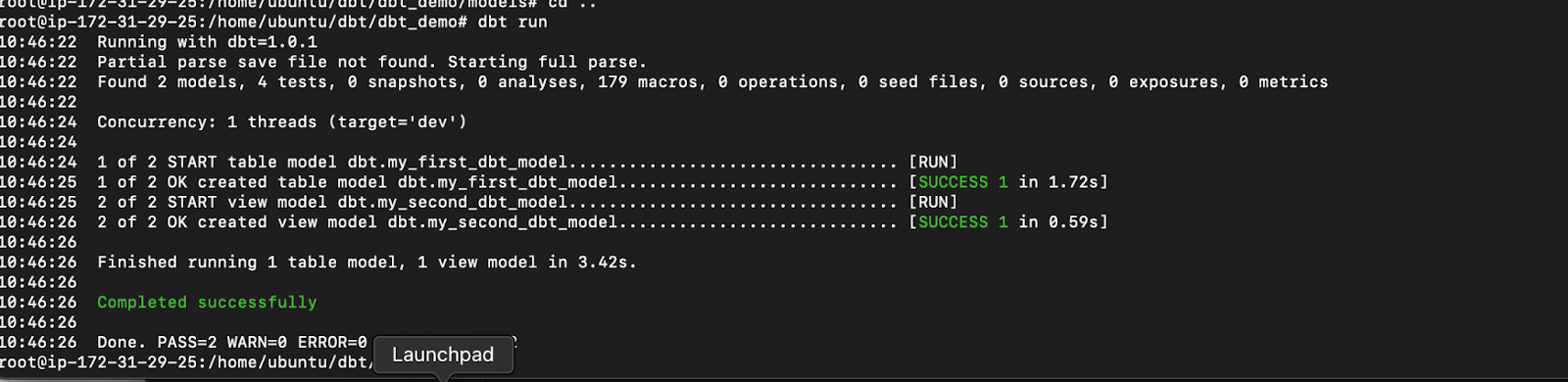
(vii) Run DBT run command to execute the
Command:
1
dbt run
Result:
(viii) Verify the first and second model created in the snowflake.
1
Select * from "ANALYTICS"."DBT"."MY_FIRST_DBT_MODEL";
Summary
In this post, we discussed how to set up a DBT on an EC2 instance and connect to the snowflake and implemented a simple transformation logic by creating a new table in the Database.
Use Case:
DBT tool is used to Create the table or view based on the select query. With DBT, data teams work directly within the warehouse to produce trusted datasets for reporting, ML modeling, and operational workflows.
If you enjoy the article, Please Subscribe.